Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMZC90K)
| Drug Name |
Vitamin E
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Covi-ox; VITAMIN E; E-Vimin; Syntopherol; Profecundin; Evitaminum; Viprimol; Vascuals; Etamican; Viteolin; Tokopharm; Vitayonon; Epsilan; Emipherol; Denamone; Almefrol; Verrol; Ilitia; Etavit; 77171-98-3; Evion; Esorb; alpha-Tokoferol; alpha Tocopherol; Vitaplex E; Vitamin E alpha; Eprolin S; Viterra E; E Prolin; Spavit E; Vita E; Endo E; Med-E; Lan-E; Antisterility vitamin; alpha-Tocopherol acid; Tenox GT 1; (R)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-((4S,8S)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)chroman-6-ol; Rhenogran Ronotec 50; Vi-E; Covitol F 1000; E 307 (tocopherol)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Humans and other mammals
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
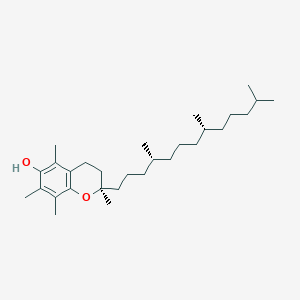 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 2 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 430.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 10.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Vitamin E (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
